In the previous lesson, we have learned how to write code using various mathematical functions in Visual Basic 2019. In this lesson, we shall proceed to learn how to work with a group of mathematical functions that deal with angles and lengths of a polygon, the trigonometric functions. The three basic trigonometric functions are Sin, Cos, and Tan which stand for sine, cosine, and tangent. We also deal with the inverse trigonometric functions Asin, Acos, and Atan respectively.
The Sin function returns the sine value of an angle. We need to convert the angle to radian as Visual Basic 2019 cannot deal with an angle in degree. The conversion is based on the following equation:
π radian= 180º
so 1º=π/180 radian
The issue is how to get the exact value of π? We can use π=3.14159 but it will not be accurate. To get the exact value of π, we use the arcsine function, i.e. is Asin.
Using the equation
sin(π/2)=1, Asin(1)=π/2
therefore,
π=2Asin(1)
The syntax of the Sin function in Visual Basic 2019 is
Math.Sin(Angle in radian)
In this example, we use pi to represent π and assign the value of π using the formula pi = 2*Math.Asin(1). We use the function Round to round the value of sine to four decimal places.
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
Dim pi As Single
pi = 2*Math.Asin(1)
MsgBox("Sin 90 is" & Math.Round(Math.Sin(pi / 2), 4))
End Sub

In Visual Basic 2019, the Cos function returns the Cosine value of an angle. The syntax is
Math.Cos(Angle in radian)
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
Dim pi As Single
pi = 2*Math.Asin(1)
MsgBox("Cos 180 is " & Math.Round(Math.Cos(pi), 4))
End Sub

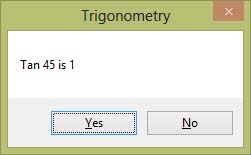
In Visual Basic 2019, the Tan function returns the tangent value of an angle. The syntax is
Math.Tan(Angle in radian)
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
Dim pi As Single
pi = 2 * Math.Asin(1)
MsgBox("Tan 45 is " & Math.Round(Math.Tan(pi / 4)), 4)
End Sub
The Asin function returns the value of arcsine (inverse sine ) and it represents the angle that corresponds to the sine value. For example, sin90º = 1, so asin(1)=90º
In Visual Basic 2019, the value of arcsine is expressed in terms of radian. To convert the value to degree, we use the formula 1 radian=180º/π, where π=2Asin(1).
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button7.Click
Dim pi As Single
pi = 2 * Math.Asin(1)
MsgBox("Asin(1)is " & Math.Round(Math.Asin(1) * 180 / pi), 4)
End Sub

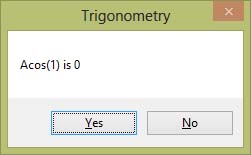
In Visual Basic 2019, the Acos function returns the value of arc cosine (inverse cosine ) and it represents the angle that corresponds to the cos value. For example, cos90º = 0, so acos(0)=90º
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button7.Click
Dim pi As Single
pi = 2 * Math.Asin(1)
MsgBox("Asin(1)is " & Math.Round(Math.Acos(1) * 180 / pi), 4)
End Sub
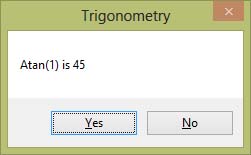
In Visual Basic 2019, the Atan function returns the value of arc tangent (inverse tangent) and it represents the angle that corresponds to the tan value. For example, tan45º = 1, so atan(1)=45º
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button7.Click
Dim pi As Single
pi = 2 * Math.Asin(1)
MsgBox("Asin(1)is " & Math.Round(Math.Atan(1) * 180 / pi), 4)
End Sub
Trigonometric functions can be used to solve various mathematical problems. Common examples are problems involving the sine rule, the cosine rule, trigonometric identities, trigonometric equations, the projectile equation and more.
For example, in a triangle ABC, give angle A=60 and angle B=30 respectively, length BC denoted by a=4 you can calculate length AC (denoted by b).
The formula is
a/sinA=b/sinB, so b=asinB/sinA
Private Sub Button8_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button8.Click
Dim pi As Single
Dim A As Single, B As Single, x As Single
pi = 2 * Math.Asin(1)
A = 60 * pi / 180
B = 40 * pi / 180
x = 4
MsgBox("AC= " & Math.Round((x * Math.Sin(A) / Math.Sin(B)), 4))
End Sub
Copyright©2008 Dr.Liew Voon Kiong. All rights reserved |Contact|Privacy Policy