Lesson 13: If..Then..Else in VB2019
Master conditional logic to create intelligent applications
Key Takeaway
The If..Then..Else structure is fundamental to programming, allowing your applications to make decisions based on conditions and execute different code paths.
In this lesson, we'll learn about conditional operators and logical operators along with the powerful If..Then..Else keywords that form the backbone of decision-making in Visual Basic 2019.
13.1 Conditional Operators
Conditional operators resemble mathematical operators. These operators allow a Visual Basic 2019 program to compare data values and decide what actions to take. They are also known as numerical comparison operators.
| Operator | Description | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| = | Equal to | 5 = 5 | True |
| > | Greater than | 10 > 5 | True |
| < | Less than | 5 < 10 | True |
| >= | Equal to or Greater than | 10 >= 10 | True |
| <= | Less than or Equal to | 5 <= 10 | True |
| <> | Not equal to | 5 <> 10 | True |
13.2 Logical Operators
When you need to make more than one comparison to arrive at a decision, logical operators become essential. They can compare both numerical data and non-numeric data such as strings.
| Operator | Description | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| And | Both sides must be true | (5 > 3) And (10 > 5) | True |
| Or | One side or other must be true | (5 > 10) Or (10 > 5) | True |
| Xor | One side or other must be true but not both | (5 > 3) Xor (10 < 5) | True |
| Not | Negates true | Not (5 > 10) | True |
String Comparison Rules
When comparing strings: uppercase letters are less than lowercase letters, "A" < "B" < "C" ... < "Z", and numbers are less than letters.
13.3 If Control Structure
To control program flow and make decisions, we use the If control structure with conditional and logical operators. There are three types:
Executes code only if condition is true
If condition Then
' Code to execute
End If
Executes one block if true, another if false
If condition Then
' True code
Else
' False code
End If
Handles multiple conditions sequentially
If condition1 Then
' Code 1
ElseIf condition2 Then
' Code 2
Else
' Default code
End If
13.3(a) If...Then Statement
This structure executes code only when the condition is true. If false, no action is performed.
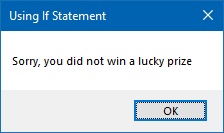
Example 13.1: Number Checker
This program checks if a number is between 50 and 100. If true, it shows a winning message. Otherwise, it shows a different message.
Private Sub BtnCheck_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnCheck.Click Dim myNumber As Integer myNumber = TxtNum.Text ' Check if number is between 50 and 100 If myNumber >= 50 And myNumber < 100 Then MsgBox("Congratulations! You win a lucky prize") End If ' Check if number is outside the range If myNumber < 50 Or myNumber >= 100 Then MsgBox("Sorry, you did not win a lucky prize") End If End Sub
Output:


13.3(b) If...Then...Else Statement
This structure provides a cleaner way to handle true/false conditions by executing one block when true and another when false.
Example 13.2: Improved Number Checker
This improved version uses If...Then...Else to provide both outcomes in a single structure.
Private Sub BtnCheck_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnCheck.Click Dim myNumber As Integer myNumber = TxtNum.Text If myNumber >= 50 And myNumber < 100 Then MsgBox("Congratulations! You win a lucky prize") Else MsgBox("Sorry, you did not win a lucky prize") End If End Sub
Output:
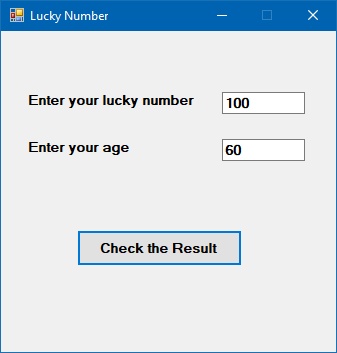
Example 13.3: Dual Condition Check
This program checks two conditions: number must be at least 100 AND age must be at least 60 to win a prize.
Private Sub BtnCheck_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnCheck.Click Dim myNumber, myAge As Integer myNumber = TxtNum.Text myAge = TxtAge.Text ' Both conditions must be true to win If myNumber >= 100 And myAge >= 60 Then MsgBox("Congratulations! You win a lucky prize") Else MsgBox("Sorry, You did not win any prize") End If End Sub
Output:
13.3(c) If...Then...ElseIf Statement
When you need to handle multiple conditions, the If...Then...ElseIf structure provides an efficient solution.
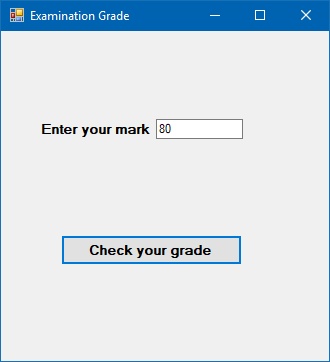
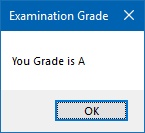
Example 13.4: Grade Calculator
This program calculates a letter grade based on a numerical mark using ElseIf statements.
Private Sub BtnCalculate_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnCalculate.Click Dim mark As Integer Dim grade As String mark = TxtMark.Text If mark >= 80 And mark <= 100 Then grade = "A" ElseIf mark >= 60 And mark < 80 Then grade = "B" ElseIf mark >= 40 And mark < 60 Then grade = "C" ElseIf mark >= 0 And mark < 40 Then grade = "D" Else grade = "Out of Range" End If MsgBox("Your Grade is " & grade) End Sub
Output:
Lesson Summary
In this lesson, you've mastered the fundamentals of conditional logic in Visual Basic 2019:
Conditional Operators
Learned to use =, >, <, >=, <=, <> for value comparisons
Logical Operators
Mastered And, Or, Xor, and Not for complex conditions
If Control Structures
Implemented If...Then, If...Then...Else, and If...Then...ElseIf statements
Practical Applications
Built a number checker, dual condition validator, and grade calculator
Conditional logic is essential for creating intelligent applications. In the next lesson, we'll explore the Select Case statement for more efficient multi-condition handling.
Next Lesson
Ready to learn about efficient multi-condition handling? Continue to Lesson 14: Select Case.
Related Resources

Visual Basic 2019 Made Easy
Unlock the power of Visual Basic 2019 with this comprehensive, easy-to-follow handbook written by Dr. Liew, renowned educator and founder of the popular programming tutorial website VBtutor.net. Whether you're new to programming or brushing up your skills, this book is your perfect companion to learn Visual Basic 2019 from the ground up.
What You'll Learn:
- Understand Core Programming Concepts: Grasp the foundational principles of Visual Basic 2019, including variables, data types, conditional logic, loops, and event-driven programming.
- Develop Real Windows Desktop Applications: Build fully functional and interactive Windows apps using Visual Studio 2019—guided through step-by-step tutorials.
- Apply Dozens of Ready-to-Use Examples: Explore a rich collection of practical sample programs, from basic calculators to image viewers and database applications.
- Adapt and Reuse Code for Your Own Projects: Customize professionally written code snippets to speed up your development process and bring your ideas to life.
- Package and Deploy Like a Pro: Learn how to compile, test, and distribute your Visual Basic applications seamlessly with built-in deployment tools.

Visual Basic Programming With Code Examples
Visual Basic Programming with Code Examples offers a unique dual-format approach, showcasing sample codes in both Visual Basic 6 (VB6) and VB.NET. This side-by-side presentation helps you understand the evolution of Visual Basic and empowers you to work confidently across both environments.
What You'll Learn:
- Core Concepts Made Easy: Explore data types, control structures, file handling, procedures, user interface design, and more.
- Hands-On Application Building: Design real-world applications, including financial calculators, educational tools, games, multimedia apps, and database systems.
- 48 Practical Code Examples: Study and customize fully explained programs that illustrate key programming techniques.
- Dual-Code Format: Learn to translate and adapt code between VB6 and VB.NET seamlessly.