In Visual Basic 2019, looping involves a procedure that runs iteratively until a certain condition is met. For example, we can design a program that adds a series of numbers until the sum exceeds a certain value. You can also create a VB 2019 program that asks the user to enter data repeatedly until he or she enters the word 'Finish'. There are three types of Loops, namely the For…..Next loop, the Do loop, and the While…..End While loop
The structure of the For...Next loop is as shown below:
For counter=startNumber to endNumber (Step increment) One or more statements Next
In order to exit a For…..Next Loop, you can place the Exit For statement within the loop. It is usually used together with the If….Then statement. For its application, you can refer to example 15.1 d.
Dim counter as Integer For counter=1 to 10 ListBox1.Items.Add (counter) Next* The program will enter number 1 to 10 into the list box.
Dim counter , sum As Integer For counter=1 to 100 step 10 sum+=counter ListBox1.Items.Add (sum) Next
This program will compute a series of subtractions as follow:
1000-100-95-90-………-5. In this case, the increment is negative.
Dim counter, sum As Integer sum = 1000 For counter = 100 To 5 Step -5 sum – = counter ListBox1.Items.Add(sum) Next
This program uses Exit ...For to escape the loop when n is greater than 6.
Dim n as Integer For n=1 to 10 If n>6 then Exit For End If Else ListBox1.Items.Add ( n) Next End If Next
In VB2019, there are several Do Loop structures, as shown below:
a) Do While condition Block of one or more statements Loop b) Do Block of one or more statements Loop While condition c) Do Until condition Block of one or more statements Loop d) Do Block of one or more statements Loop Until condition
We can also use Exit Do to escape the loop.
Let' s examine the following examples:
In this example, the procedure will keep on adding the initial number by 1 until it exceeds 1000.
Do while counter <=1000 TextBox1.Text=counter counter +=1 Loop
We can rewrite the procedure above and achieve the same result. The code is shown as follows:
Do TextBox1.Text=counter counter+=1 Loop until counter>1000
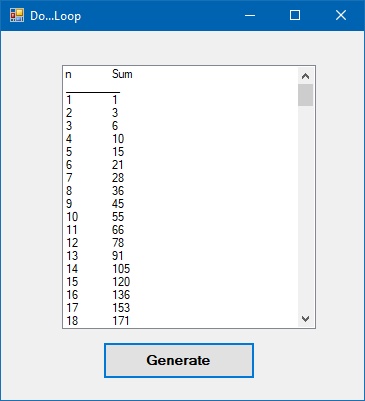
In this example, the procedure will generate two series in a list box. The first series starts with 1 and end with 100. The second series sums up the numbers in the first series. The process stops when it has repeated 100 times.
Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
Dim sum, n As Integer
ListBox1.Items.Add("n" & vbTab & "Sum")
ListBox1.Items.Add("———————-")
Do
n += 1
sum += n
ListBox1.Items.Add(n & vbTab & sum)
If n >10 Then
Exit Do
End If
Loop
End Sub
* The loop in the above example can be replaced by the following loop:
Do Until n = 100 n += 1 sum += n ListBox1.Items.Add(n & vbTab & sum) Loop
The output is as shown in Figure 15.1
The structure of a While….End While Loop is very similar to the Do Loop. it takes the following form:
While conditions statements End While
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
Dim sum, n As Integer
ListBox1.Items.Add("n" & vbTab & "sum")
ListBox1.Items.Add("———————-")
While n <> 10
n += 1
sum += n
ListBox1.Items.Add(n & vbTab & sum)
End While
End Sub
Copyright©2008 Dr.Liew Voon Kiong. All rights reserved |Contact|Privacy Policy