In Visual Basic 2019, we can write code to instruct the computer to perform mathematical calculations that involve the use of various arithmetic operators. For example, you can write programs to calculate the area of a triangle, solve simultaneous equations, plot quadratic function graph, simulate simple harmonic motion and more. Visual Basic 2019 arithmetic operators are very similar to the normal arithmetic operators, albeit some little variations. The plus and minus operators are the same while the multiplication operator uses the * symbol and the division operator use the / symbol.
The list of Visual Basic 2019 arithmetic operators are shown in Table 11.1 below:
| Operator | Mathematical Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | 1+2=3 |
| - | Subtraction | 10-4=6 |
| ^ | Exponential | 3^2=9 |
| * | Multiplication | 5*6=30 |
| / | Division | 21/7=3 |
| Mod | Modulus(returns the remainder of an integer division) | 15 Mod 4=3 |
| \ | Integer Division(discards the decimal places) | 19/4=4 |
In this program, you insert two text boxes, four labels, and one button. In the properties windows, change the name of the button to BtnCal, the names of text boxes to TxtNum1 and TxtNum2 and change the names of labels to LblSum, LblDiff, LblPdct, and LblQuo respectively. Click the button and enter the code window and type the code as shown below.
Private Sub BtnCal_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles BtnCal.Click Dim num1, num2, difference, product, quotient As Single Dim num1 As Single, num2 As Single Dim sum As Single, diff As Single, pdct As Double, quo As Double num1 = TxtNum1.Text num2 = TxtNum2.Text sum=num1+num2 difference=num1-num2 product = num1 * num2 quotient=num1/num2 LblSum.Text=sum LblDiff.Text=difference LblPdct.Text = product LblQuo.Text = quotient End Sub
Upon running the program, the user may enter two numbers and click on the calculate button to perform the four basic arithmetic operations. The results will be displayed the on the four labels, as shown in Figure 11.1
This program involves the use of Pythagoras Theorem to calculate the length of hypotenuse c given the length of the adjacent side a and the length of the opposite side b. In case you have forgotten the formula for the Pythagoras Theorem, it is written as c^2=a^2+b^2 in VB2019 syntax. In this program, insert two text boxes for the user to enter the value of side a and the value of side b respectively. Add a label to display the result, which is the length of the hypotenuse. Lastly, add a button and change its name to BtnCal and its text to Calculate. Click on the Calculate button and enter the following code.
Private Sub BtnCal_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
'To draw a triangle at runtime
Dim myPen As Pen
Dim A As New Point(10, 10)
Dim B As New Point(100, 50)
Dim C As New Point(60, 150)
Dim myPoints As Point() = {A, B, C}
myPen = New Pen(Drawing.Color.Blue, 5)
Dim myGraphics As Graphics = Me.CreateGraphics
myGraphics.DrawPolygon(myPen, myPoints)'Pythagoras equation
Dim a1, b1, c1 As Single
a1 = TxtA.Text
b1 = TxtB.Text
c1 = (a1 ^ 2 + b1 ^ 2) ^ (1 / 2)
LblC.Text = c1
End Sub
* The first part of the code is to draw a triangle at runtime. You shall learn how to write code to draw a triangle in a later lesson. The output is shown in Figure 11.2
A lot of people are obese now and it could affect their health seriously. Obesity has proven by medical experts to be one of the main factors that bring many adverse medical problems, including cardiovascular disease. If your BMI is more than 30, you are considered obese. You can refer to the following range of BMI values for your weight status.
Underweight = <18.5 Normal weight = 18.5-24.9 Overweight = 25-29.9 Obesity = BMI of 30 or greater
BMI can be calculated using the formula weight/( height )^2, where weight is measured in kg and height in meter. If you only know your weight and height in lb and feet, then you need to convert them to the metric system. The code is shown below:
Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArsgs) Handles Button1.ClickDim height, weight, bmi As Single height = TextBox1.Text weight = TextBox2.Text bmi = (weight) / (height ^ 2) LblBMI.Text = bmi End Sub
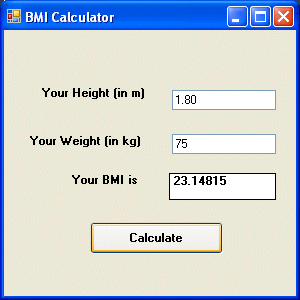
The output is shown in the Figure 11.3 below. In this example, height is 1.80m( about 5 foot 11), weight is 75 kg( about 168Ib), and BMI is about 23.14815. The reading suggests that the person is healthy. (Note; 1 foot=0.3048, 1 lb=.45359237 kilogram)
From the above examples, you can see that writing code that involves arithmetic operations is relatively easy. Here are more arithmetic projects you work on in Visual Basic 2019:
Area of a triangle Area of a rectangle Area of a circle Volume of a cylinder Volume of a cone Volume of a sphere Compound interest Future value Mean Variance Sum of angles in polygons Conversion of lb to kg Conversion of Fahrenheit to Celsius Conversion of mile to km Conversion of meter to foot
Copyright©2008 Dr.Liew Voon Kiong. All rights reserved |Contact|Privacy Policy