We can create a Visual Basic procedure that enables the program to run iteratively until specific conditions are satisfied. This procedure is commonly referred to as looping. Looping is an invaluable feature of Visual Basic as it simplifies repetitive tasks and enhances efficiency. There are three kinds of loops in Visual Basic, the Do...Loop ,the For.......Next loop and the While.....Wend Loop.
The Do Loop statements have four different forms, as shown below:
Do While condition Block of one or more VB statements Loop
Do Block of one or more VB statements Loop While condition
Do Until condition Block of one or more VB statements Loop
Do Block of one or more VB statements Loop Until condition
Do while counter <=1000 num.Text=counter counter =counter+1 Loop
* The above example will keep on adding until counter > 1000
The above example can be rewritten as
Do counter=counter+1 Loop until counter>1000
Sometime we need exit to exit a loop earlier when a certain condition is fulfilled. The keyword to use is Exit Do. You can examine Example 9.2 for its usage.
Dim sum, n as Integer Private Sub Form_Activate() List1.AddItem "n" & vbTab & "sum" Do n=n+1 sum=sum+n-resize List1.AddItem n & vbTab & sum If n=100 Then Exit Do End If Loop End Sub
Explanation
In the above example, we compute the summation of 1+2+3+4+……+100. In the design stage, you need to insert a ListBox into the form for displaying the output, named List1. The program uses the AddItem method to populate the ListBox. The statement List1.AddItem "n" & vbTab & "sum" will display the headings in the ListBox, where it uses the vbTab function to create a space between the headings n and sum.
The For....Next Loop event procedure is written as follows:
For counter=startNumber to endNumber (Step increment) One or more VB statements Next
Private Sub Command1_Click() Dim counter As Integer For counter = 1 To 10 List1.AddItem counter Next End Sub
Private Sub Command1_Click() Dim counter As Integer For counter = 1 To 1000 Step 10 counter = counter + 1 Print counter Next End Sub
For counter=1000 to 5 step -5 counter=counter-10 If counter<50 then Exit For Else Print "Keep Counting" End If Next
Private Sub Form_Activate( ) For n=1 to 10 If n>6 then Exit For Else Print n Enf If Next End Sub
Sometimes the user might want to get out from the loop before the whole repetitive process is executed, the command to use is Exit For. To exit a For….Next Loop, you can place the Exit For statement within the loop; and it is normally used together with the If…..Then… statement. Its usages is shown in Example 9.3 d.
When you have a loop within a loop, then you have created a nested loop. You can actually have as many loops as you want in a nested loop provided the loops are not the never-ending type. For a nested loop that consists of two loops, the first cycle of the outer loop will be processed first, then it will process the whole repetitive process of the inner loop, then the second cycle of the outer loop will be processed and again the whole repetitive process of the inner loop will be processed. The program will end when the whole cycle of the outer loop is processed.
The Structure of a nested loop is :
For counter1=startNumber to endNumber (Step increment) For counter2=startNumber to endNumber (Step increment) One or more VB statements Next counter2 Next counter1
Private Sub Form_Activate ( ) For firstCounter= 1to 5 Print "Hello" For secondCounter=1 to 4 Print "Welcome to the VB tutorial" Next secondCounter Next firstCounter Print"Thank you" End Sub
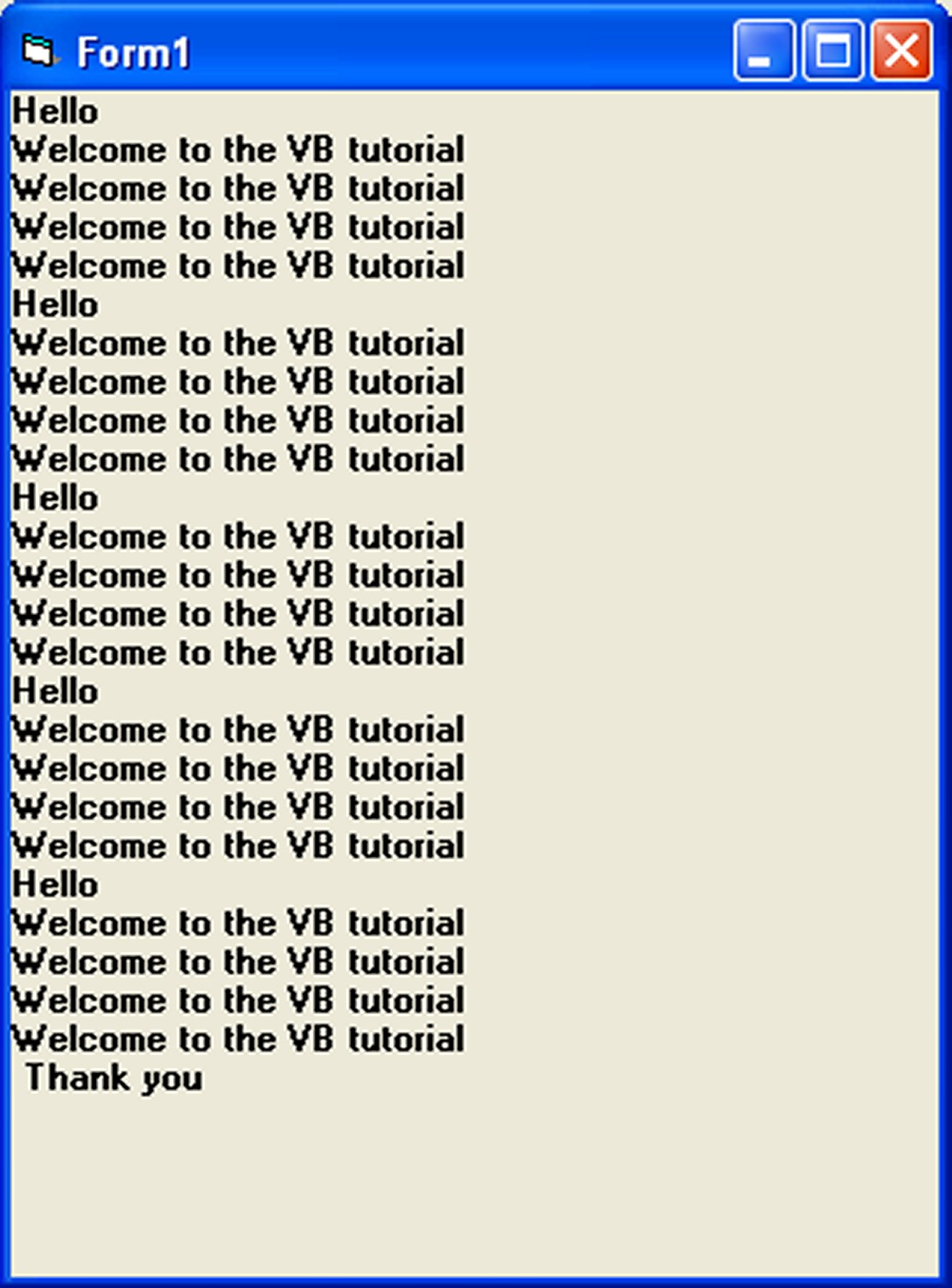
The output of the above program is shown in Figure 9.1. As the outer loop has five repetitions, it will print the word “Hello” five times. Each time after it prints the word “Hello”, it will print four lines of the “Welcome to the VB tutorial” sentences as the inner loop has four repetitions.
The structure of a While….Wend Loop is very similar to the Do Loop. it takes the following form:
While condition Statements Wend
The above loop means that while the condition is not met, the loop will go on. The loop will end when the condition is met. Let’s examine the program listed in example 9.4.
Dim sum, n As Integer Private Sub Form_Activate() List1.AddItem "n" & vbTab & "sum" While n <> 100 n = n + 1 Sum = Sum + n List1.AddItem n & vbTab & Sum Wend End Sub
Copyright©2008 Dr.Liew Voon Kiong. All rights reserved |Contact|Privacy Policy
Last update:11/19/2023 09:00:32