Mathematical functions play a crucial role in programming due to their inherent usefulness and importance. In programming, we frequently encounter various mathematical concepts that necessitate their utilization. These concepts encompass probability and chance, variables, logical operations, calculations, coordinates, time intervals, and much more. Hence, a firm grasp of mathematical functions is essential for effectively tackling these programming challenges. The common mathematical functions in Visual Basic 6 are Rnd, Sqr, Int, Abs, Exp, Log, Sin, Cos, Tan , Atn, Fix and Round.
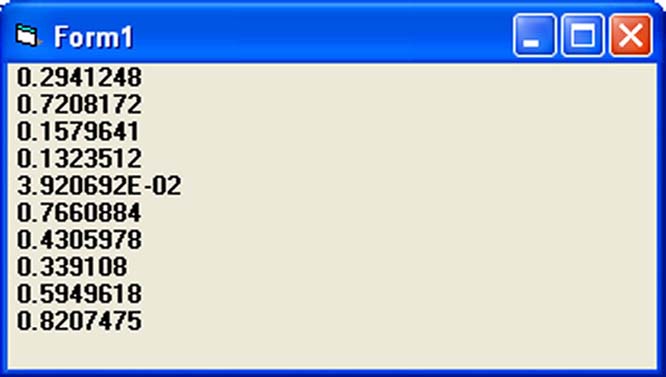
Rnd is is very useful function for dealing with the concept of chance and probability. The Rnd function returns a random value between 0 and 1. In Example 11.1. When you run the program, you will get an output of 10 random numbers between 0 and 1. Randomize Timer is to randomize the process.
Private Sub Form_Activate Dim x as integer For x=1 to 10 Print Rnd Next End Sub
Random numbers in their original forms are not very useful in programming until we convert them to integers. For example, if we need to obtain a random output of 6 random integers ranging from 1 to 6, which make the program behaves as a virtual die, we need to convert the random numbers using the format Int(Rnd*6)+1. Let’s study the following example:
In this example, Int(Rnd*6) will generate a random integer between 0 and 5 because the function Int truncates the decimal part of the random number and returns an integer. After adding 1, you will get a random number between 1 and 6 every time you click the command button. For example, let say the random number generated is 0.98, after multiplying it by 6, it becomes 5.88, and using the integer function Int(5.88) will convert the number to 5; and after adding 1 you will get 6.
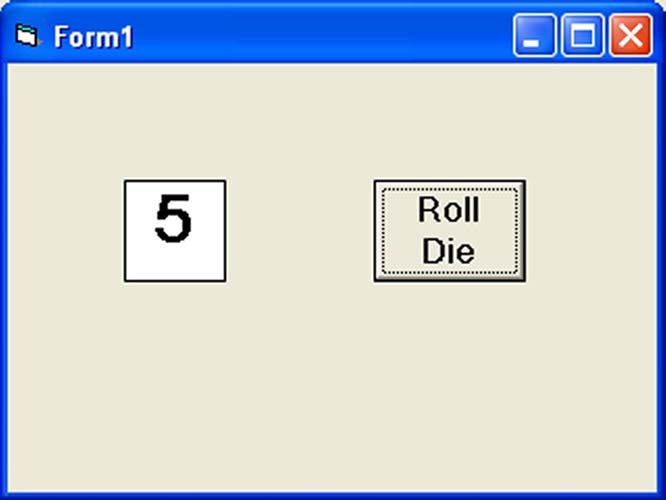
In this example, you place a command button and change its caption to ‘roll die’. You also need to insert a label into the form and clear its caption at the designing phase and make its font bigger and bold. Then set the border value to 1 so that it displays a border; and after that set the alignment to center. The statement Label1.Caption=Num means the integer generated will be displayed as the caption of the label.
Dim num as integer Private Sub Command1_Click( ) Num=Int(Rnd*6)+1 Label1.Caption=Num End Sub
Now, run the program and then click on the roll die button, you will get an output like the Figure 11.2 below:
The numeric functions are Int, Sqr, Abs, Exp, Fix, Round and Log.
a) Int is the function that converts a number into an integer by truncating its decimal part and the resulting integer is the largest integer that is smaller than the number. For example, Int(2.4)=2, Int(4.8)=4, Int(-4.6)= -5, Int(0.032)=0 and so on.
b) Sqr is the function that computes the square root of a number. For example, Sqr(4)=2, Sqr(9)=2 and etc.
c) Abs is the function that returns the absolute value of a number. So Abs(-8) = 8 and Abs(8)= 8.
d) Exp of a number x is the value of ex. For example, Exp(1)=e1 = 2.7182818284590
e) Fix and Int are the same if the number is a positive number as both truncate the decimal part of the number and return an integer. However, when the number is negative, it will return the smallest integer that is larger than the number. For example, Fix(-6.34)= -6 while Int(-6.34)=-7.
f) Round is the function that rounds up a number to a certain number of decimal places. The Format is Round (n, m) which means to round a number n to m decimal places. For example, Round (7.2567, 2) =7.26
g) Log is the function that returns the natural Logarithm of a number. For example,
Log 10= 2.302585
This example computes the values of Int(x), Fix(x) and Round(x,n) in a table form. It uses the Do Loop statement and the Rnd function to generate 10 numbers. The statement x = Round (Rnd * 7, 7) rounds a random number between 0 and 7 to 7 decimal places. Using commas in between items will create spaces between them and hence a table of values can be created. The program and output are shown below
Private Sub Form_Activate () Dim n As Integer Dim x As Single n = 1 Print "n","x","Int(x)", "Fix(x)", "Round(x, 4)" Do While n <11 x = Round (Rnd* 7, 7) Print n, x, Int(x), Fix(x), Round(x, 4) n = n + 1 Loop End Sub

Copyright©2008 Dr.Liew Voon Kiong. All rights reserved |Contact|Privacy Policy