In this lesson, we shall learn about the conditional operators and the logical operators involving the use of the If..Then...Else keywords.
Conditional operators allow a Visual Basic 2022 program to compare data values and then decide what actions to be taken. They are used to compare two values to see whether they are equal, one value is greater than the other value or one value is less than the other value. The comparison will return a true or false result. These operators are shown in Table 13.1
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| = | Equal to |
| > | Greater than |
| < | Less than |
| >= | Equal to or Greater than |
| <= | Less than or Equal to |
| <> | Not equal to |
In certain cases, we might need to make more than one comparisons to arrive at a decision. In this case, using conditional operators alone might not be sufficient and we need to use the logical operators, as shown in Table 13.2. Logical operators can be used to compare numerical data as well as non-numeric data such as strings. In making strings comparison, there are certain rules to follows: Upper case letters are less than lowercase letters, "A"<"B"<"C"<"D"…….<"Z" and number are less than letters.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| And | Both sides must be true |
| Or | One side or other must be true |
| Xor | One side or other must be true but not both |
| Not | Negates true |
To control the Visual Basic 2022 program flow and to make decisions, we shall use the If control structure together with the conditional operators and logical operators. There are three types of If control structures, namely If….Then statement, If….Then… Else statement and If….Then….ElseIf statement.
This control structure instructs the computer to perform a certain action specified by the Visual Basic 2022 expression if the condition is true. However, when the condition is false, no action will be performed. The syntax for the if...then statement is
If condition Then Visual Basic 2022 expressions End If
In this program, we insert a TextBox and rename it as txtNum and a Button and rename it to BtnCheck. We write the code so that when the user runs the program and enter a number that is greater than or equal to 50 and less than 100, he or she will win a lucky prize. On the other hand, if the number entered is less than 50 or more than or equal to 100, the user will not win any prize. This program involves the use of the If and then keywords, the conditional operators and the logical operators Or and And.
Private Sub BtnCheck_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnCheck.Click
Dim myNumber As Integer
myNumber = TxtNum.Text
If myNumber >= 50 And myNumber < 100 Then
MsgBox("Congratultaion! You win a lucky prize")
End If
If myNumber < 50 Or myNumber >= 100 Then
MsgBox("Sorry, you did not win a lucky prize")
End If
End Sub
The output is as shown in Figure 13.1 and Figure 13.2

Clicking the Check the Result produces the following message:
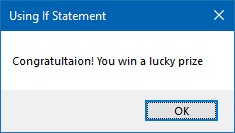
If you key in a number that is <50 and >=100, you will get the following message:

As we can see in example 13.1, we need to use two sets of If...Then statements to provide alternative outputs. However, there is a simpler way to provide alternative output, which is to use the If...Then...Else Statement. This control structure will ask the computer to perform a certain action specified by the Visual Basic 2017 expression if the condition is met. And when the condition is false , an alternative action will be executed. The syntax for the if…then... Else statement is
If condition Then Visual Basic 2022 expression 1 Else Visual Basic 2022 expression 2 End If
We modified the code in Example 13.1 by deleting the second If statement and use the Else keyword instead. When you run the program and enter a number that is greater than 100, the message “Congratulation! You win a lucky prize” will be shown.Otherwise, you will see the "Sorry, You did not win any prize" message, as shown in Figure 13.3
Private Sub OK_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles OK.Click Dim myNumber As Integer myNumber = TxtNum.Text If myNumber >= 50 And myNumber < 100 Then MsgBox( "Congratulation! You win a lucky prize") Else MsgBox( "Sorry, You did not win a lucky prize") End If End Sub
The program will produce the same results as in Example 13.1
This program involves using two variables and two conditions. Both conditions must be met otherwise the second block of code will be executed. In this example, the number entered must at least 100 and the age must be at least 60 in order to win a lucky prize, any one of the above conditions not fulfilled will disqualify the user from winning a prize. You need to add another text box for the user to enter his or her age. The output is as shown in Figure 13.4
Private Sub OK_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles OK.Click
Dim myNumber, MyAge As Integer
myNumber = TxtNum.Text
MyAge = TxtAge.Text
If myNumber >= 100 And MyAge >=60 Then
MsgBox(" Congratulation! You win a lucky prize")
Else
MsgBox("Sorry, You did not win any prize")
End If
End Sub

If you number is 100 and age is 60, you win a lucky price.
In circumstances where there are more than two alternative conditions, using just If….Then….Else statement will not be enough. In this case, we can use the If….Then…ElseIf Statement.The general structure for the if…then... Else statement is
If condition ThenVisual Basic 2017 expression1 ElseIf condition Then Visual Basic 2017 expression2 ElseIf condition Then Visual Basic 2017 expression3 .. Else Visual Basic 2017 expression4 End If
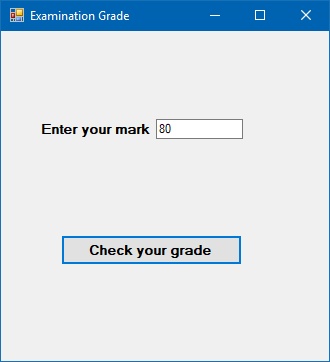
This program can compute the grade for the mark entered by the user. We use several ElseIf statements and the logical operator And to achieve the purpose. The outputs are as shown in Figure 13.5 and Figure 13.6
Private Sub OK_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles OK.Click
Dim Mark As Integer
Dim Grade As String
Mark = TxtMark.Text
If Mark >= 80 And Mark <= 100 Then
Grade = "A"
ElseIf Mark >= 60 And Mark < 80 Then
Grade = "B"
ElseIf Mark >= 40 And Mark < 60
Grade = "C"
ElseIf Mark >= 0 And Mark < 40
Grade = "D"
Else
Grade = "Out of Range"
End If
MsgBox("You Grade is " & Grade)
End Sub

Copyright©2008 Dr.Liew Voon Kiong. All rights reserved |Contact|Privacy Policy