In this lesson, we shall learn how to write Visual Basic 2017 code. First of all, you need to understand the concept of event-driven programming.
Visual Basic 2017 is an event-driven programming language, which means that the code is executed in response to events. In the previous lesson, we have learned how to design the interface by putting the controls(objects) on the form. However, they do nothing unless we write code for the objects to respond to events triggered by the user. Every control you place on the form has a set of events related to them.
The events usually comprise but not limited to the user’s inputs. Among the events are load, click, double click, drag, and drop, pressing the keys and more. To view the events, double-click the control on the form to enter the code window. The default event will appear at the top part on the right side of the code window. You need to click on the default event to view other events associated with the control. The code appears on the left side is the event procedure associated with the load event. Figure 4.1 illustrates the event procedure load associated with the default form.
 Figure 4.1: Events associated with Form
Figure 4.1: Events associated with Form
Figure 4.2 shows the events associated with button
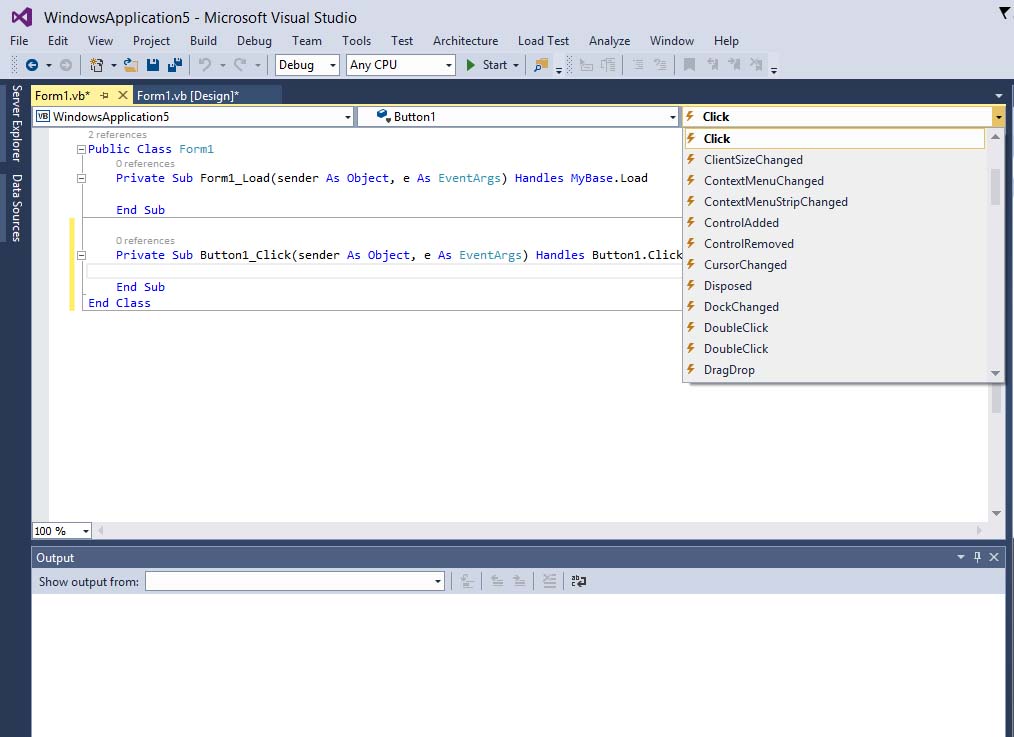
To write code in Visual Basic 2017, click on any part of the form to enter the code window as shown in Figure 4.1. This is the structure of an event procedure. In this case, the event procedure is to load Form1. It starts with Private Sub and ends with End Sub. This procedure includes the Form1 class and the event Load, and they are bound together with an underscore, i.e. Form_Load. It does nothing other than loading an empty form. To make the load event does something, insert the statement
MsgBox (“Welcome to Visual Basic 2017″)
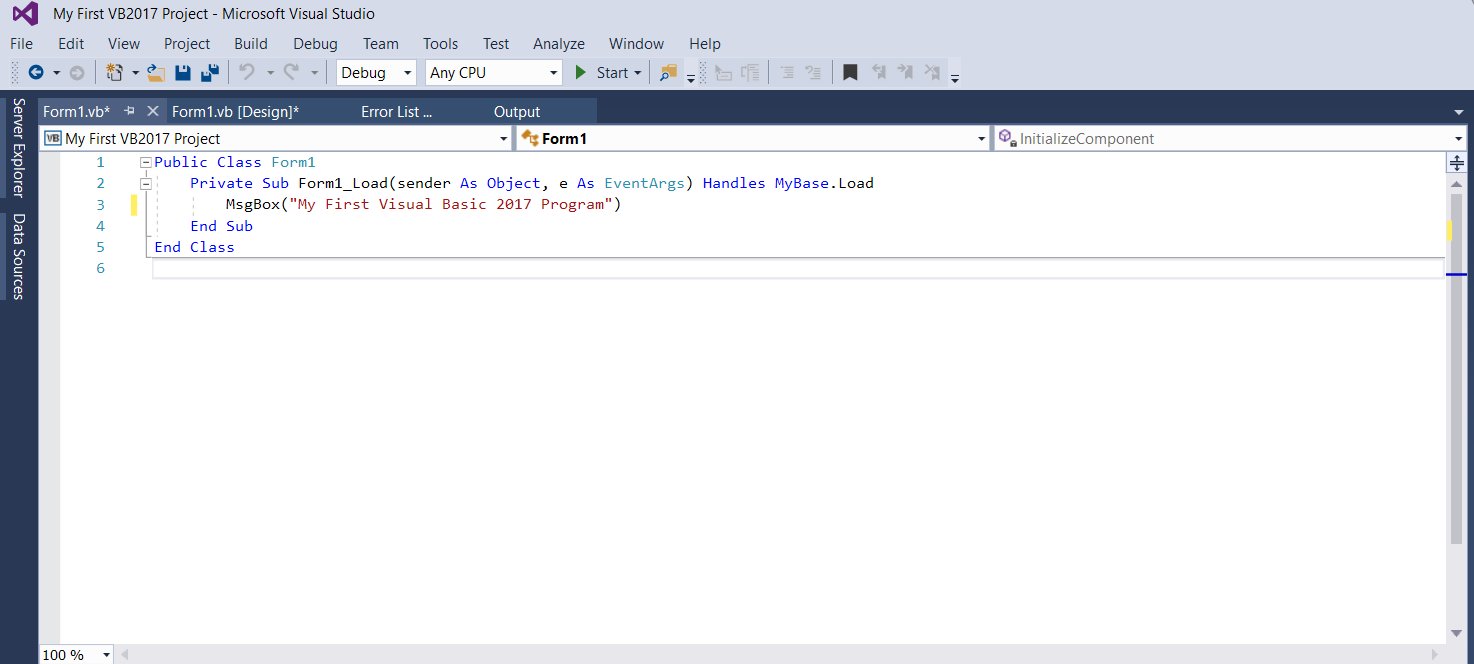
When you run the program, a message box that displays the text “My First Visual Basic 2017 Program” will appear, as shown in Figure 4.4. MsgBox is a built-in function in Visual Basic 2017 that display a message in a pop-up message box.
* You will notice that above Private Sub structure there is a preceding keyword Public Class Form1. This is the concept of an object-oriented programming language. When we start a windows application in Visual Basic 2017, we will see a default form with the name Form1 appears in the IDE, it is actually the Form1 Class that inherits from the Form class System.Windows.Forms.Form. A class has events as it creates an instance of a class or an object.
You can also write code to perform the arithmetic calculation. For example, you can use the MsgBox and the arithmetic operator plus to perform an addition of two numbers, as shown below:

*The symbol & (ampersand) is to perform string concatenation. The statement Me.Close() is to close the program after clicking the OK button.
The output is as shown in Figure 4.6

Copyright©2008 Dr.Liew Voon Kiong. All rights reserved |Contact|Privacy Policy