[Lesson 19] << [CONTENTS] >> [Lesson 21]
20.1 Introduction to Error Handling
Error handling is an essential procedure in Visual Basic 2012 programming to build an error-free program. Error-free code not only enables the programs to run smoothly and efficiently, it can also prevent all sorts of problems from happening like program crashes or system hangs.
Errors often occur due to incorrect input from the user. For example, the user might make the mistake of attempting to enter text in a textbox that is designed to handle only numeric values such as the weight of a person, the computer will not be able to perform an arithmetic calculation for text, therefore, will create an error. These errors are known as synchronous errors.
Therefore a good programmer should be more alert to the parts of the program that could trigger errors and should write errors handling code to help the user in managing the errors. Writing errors handling code is a good practice for Visual Basic 2012 programmers, so do not try to finish a program fast by omitting the errors handling code. However, there should not be too many errors handling code in the program as it creates problems for the programmer to maintain and troubleshoot the program later.
Visual Basic 2012 has improved a lot in its built-in errors handling capabilities compared to Visual Basic 6. For example, when the user attempts to divide a number by zero, Vb2012 will not return an error message but gives the ‘infinity’ as the answer (although this is mathematically incorrect because it should be undefined)
20.2 Using On Error GoTo Syntax
Visual Basic 2012 still supports the VB6 errors handling syntax, that is the On Error GoTo program_label structure. We shall now learn how to write errors handling code in Visual Basic 2012. The syntax for errors handling isOn Error GoTo program_label
where program_label is the section of code that is designed by the programmer to handle the error committed by the user. Once an error is detected, the program will jump to the program_label section for error handling.
Example 20.1: Division by Zero
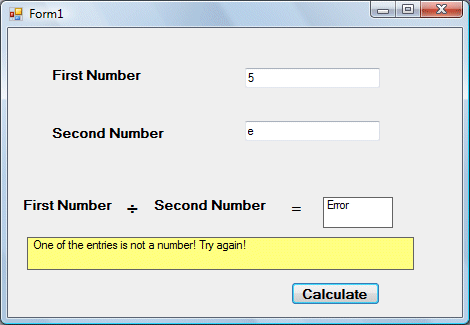
In this example, we will deal with the error of entering non-numeric data into the textboxes that suppose to hold numeric values. The program_label here is error_hanldler. when the user enters a non-numeric value into the textboxes, the error message will display the text”One of the entries is not a number! Try again!”. If no error occurs, it will display the correct answer. Try it out yourself.
The Code
Public Class Form1 Private Sub CmdCalculate_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles CmdCalculate.Click Lbl_ErrorMsg.Visible = False Dim firstNum, secondNum As Double On Error GoTo error_handler firstNum = Txt_FirstNumber.Text secondNum = Txt_SecondNumber.Text Lbl_Answer.Text = firstNum / secondNum Exit Sub 'To prevent error handling even the inputs are valid error_handler: Lbl_Answer.Text = "Error" Lbl_ErrorMsg.Visible = True Lbl_ErrorMsg.Text = " One of the entries is not a number! Try again!" End Sub End Class
The Output
20.3 Errors Handling using Try…..Catch….End Try Structure
VB2012 has adopted a new approach in handling errors or rather exceptions handling. It is supposed to be more efficient than the old On Error Goto method, where it can handle various types of errors within the Try…Catch…End Try structure.
The structure looks like this
Try statements Catch exception_variable as Exception statements to deal with exceptions End Try
Example 20.2
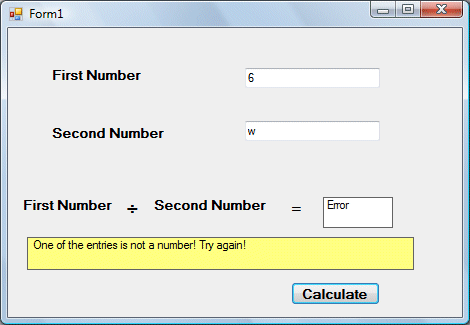
This is a modification of Example 20.1. Instead of using On Error GoTo method, we use the Try…Catch…End Try method. In this example, the Catch statement will catch the exception when the user enters a non-numeric data and return the error message. If there is no exception, there will not any action from the Catch statement and the program returns the correct answer.
The code
Public Class Form1 Private Sub CmdCalculate_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal eAs System.EventArgs) Handles CmdCalculate.Click Lbl_ErrorMsg.Visible = False Dim firstNum, secondNum, answer As Double Try firstNum = Txt_FirstNumber.Text secondNum = Txt_SecondNumber.Text answer = firstNum / secondNum Lbl_Answer.Text = answer Catch ex As Exception Lbl_Answer.Text = "Error" Lbl_ErrorMsg.Visible = True Lbl_ErrorMsg.Text = " One of the entries is not a number! Try again!" End Try End Sub End Class
The output
[Lesson 19] << [CONTENTS] >> [Lesson 21]