[Lesson 17] << [Contents] >>[Lesson 19]
In Visual Basic 2017, we can write codes that can perform arithmetic operations using standard arithmetic operators. However, for more complex mathematical calculations, we shall use the built-in mathematical functions in Visual Basic 2017. There are numerous built-in mathematical functions in Visual Basic 2017. Among them are Abs, Exp, Fix, Int, Rnd, Round, sqrt and more. We shall deal with trigonometric functions and Financial Functions in coming lessons. Most mathematical functions belong to the Math class in Visual Basic 2015. However, not all mathematical functions belong to the Math class.
18.1 The Abs function
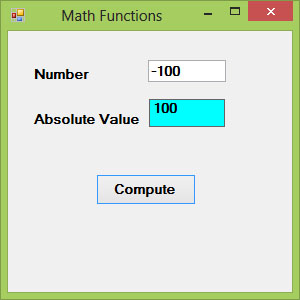
In Visual Basic 2017, the Abs function returns the absolute value of a given number.The syntax is
Math. Abs (Number)
Example 18.1
In this example, we shall add a text box control for the user to input his or her number and a label control to display the absolute value of the number. We need to use the Val function to convert text to a numeric value. Rename the textbox as TxtNum and the label as LblAbs.
The Code
Private Sub BtnComp_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnComp.Click LblAbs.Text = Math.Abs(Val(TxtNum.Text)) End Sub
The output
Figure 18.1
18.2 The Exp function
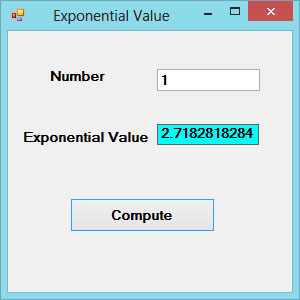
In Visual Basic 2017, the Exp function returns the exponential value of a given number. For example, Exp(1)=e=2.71828182
The syntax is
Math.Exp (Number)
Example 18.2
In this example, we shall add a text box control for the user to input his or her number and a label control to display the exponential value of the number. Rename the textbox as TxtNum and the label as LblAbs.
The Code
Private Sub BtnComp_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnComp.Click LblExp.Text = Math.Exp(Val(TxtNum.Text)) End Sub
* We use the Val function to convert a string to numeric value
The Output
Figure 18.2
18.3 The Fix Function
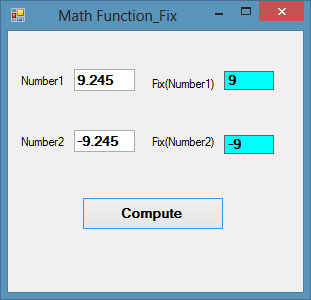
The Fix function truncates the decimal part of a positive number and returns the largest integer smaller than the number. However, when the number is negative, it returns the smallest integer larger than the number. Fix does not belong to the Math class, therefore, we do not use the Math keyword. the syntax is
Fix(number)
Example 18.3
Private Sub BtnComp_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnComp.Click LblFixNum1.Text = Fix(Val(TxtPosNum.Text)) LblFixNum2.Text = Fix(Val(TxtNegNum.Text)) End Sub
The Output
Figure 18.3
18.4 The Int Function
The Int is a function that converts a number into an integer by truncating its decimal part and the resulting integer is the largest integer that is smaller than he number. Int also does not belong to the Math class so there is no need to use the Math keyword.
For example
Int(2.4)=2, Int(6.9)=6 , Int(-5.7)=-6, Int(-99.8)=-100
18.5 The Log Function
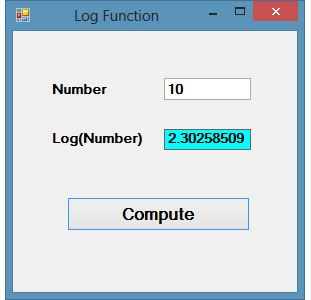
The Log function is the function that returns the natural logarithm of a number.
The syntax is
Math.Log(Number)
Example 18.4
Private Sub BtnComp_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnComp.Click LblLog.Text = Math.Log(Val(TxtNum.Text)) End Sub
Figure 18.4
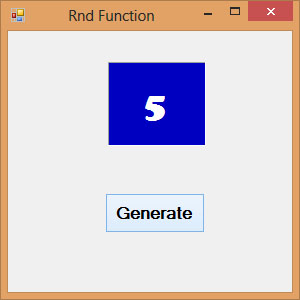
18.6 The Rnd( ) Function
Rnd is a very useful function in Visual Basic 2017. We use the Rnd function to write code that involves chance and probability. The Rnd function returns a random value between 0 and 1. Random numbers in their original form are not very useful in programming until we convert them to integers. For example, if we need to obtain a random output of 6 integers ranging from 1 to 6, which makes the program behave like a virtual dice, we need to convert the random numbers to integers using the formula Int(Rnd*6)+1.
The Rnd() function belongs to the VBMath class in Visual Basic 2015. The syntax is
VBMath.Rnd()*Number
Example 18.5
Private Sub BtnGen_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnGen.Click LblRnd.Text = Int(VBMath.Rnd() * 6) + 1 End Sub
Notice that the Rnd() function belongs to the VBMath class in Visual Basic 2015.
In this example, Int(Rnd*6) will generate a random integer between 0 and 5 because the function Int truncates the decimal part of the random number and returns an integer. After adding 1, you will get a random number between 1 and 6 every time you click the command button. For example, let say the random number generated is 0.98, after multiplying it by 6, it becomes 5.88, and using the integer function Int(5.88) will convert the number to 5, and after adding 1 you will get 6.
The Output
Figure 18.5
*We shall learn how to create an animated dice using a Timer control in later lesson
18.7 The Round Function
The Round function is the function that rounds up a number to a certain number of decimal places. The syntax is
Math.Round (number, m)
which means to round a number to m decimal places.
For example, Math.Round (7.2567, 2) =7.26
Example 18.6
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click Label1.Text = Math.Round(Val(TextBox1.Text), 2) End Sub
The Output
Figure 18.6
18.8 The Sqrt Function
The sqrt returns the square root of a number. The syntax is as follows:
Math.Sqrt(Number)
Example 18.7
Private Sub Button4_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button4.Click MsgBox(Math.Sqrt(400)) End Sub
The result is 20
[Lesson 17] << [Contents] >>[Lesson 19]