[Lesson 37]<< [Contents]
In this lesson, we shall learn how to create Visual Basic 2015 console applications using the If..Then…Else control structure and the Select Case control structure.
38.1 Using If….Then….Else
The If…Then….Else structure is as follows:
If conditions Then VB expressions Else VB expressions End If
Example 38.1
The following code uses If….Then….Else control structure to evaluate the answer entered by the user .
Sub Main()
Dim x, y, z, total As Single
Dim firstnum As String
Dim secondnum As String
Dim sum As String
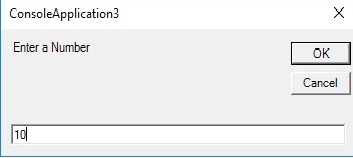
firstnum = InputBox("Enter a Number")
secondnum = InputBox("Enter a number")
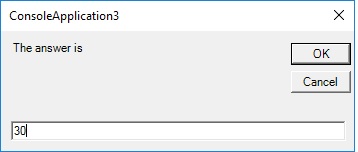
sum = InputBox("The answer is")
total = Val(firstnum) + Val(secondnum)
If total = Val(sum) Then
MsgBox("Correct")
Else
MsgBox("Wrong")
End If
End Sub
When we run the application, you will be presented with an input box as shown in Figure 38.1
Figure 38.1
After entering a number, you will be presented a second input box where you are required to enter the second number. After that, you will be presented with a third input box that prompts you to enter the answer which supposes to be the sum of the two numbers entered, as shown in Figure 38.2
Figure 38.2
If the answer is correct, a message box will display the word ‘Correct’, otherwise, it will show the word ‘Wrong’, as shown in Figure 38.3
Figure 38.3
38.2 Using Select Case
The Select Case control structure evaluates one expression for multiple values. Select Case is preferred when there exist multiple conditions.
The Select Case control structure is shown below:
Select Case expression Case value1 Block of one or more VB statements Case value2 Block of one or more VB Statements Case Else Block of one or more VB Statements End Select
Example 38.2
This application allows the user to input an examination grade and it will display the result in a message box, as shown in the figures below:
Figure 38.4
Figure 38.5