[Lesson 20] << [Contents] >> [Lesson 22]
In this lesson, we shall learn a how to use the checkbox. The Checkbox allows the user to select one or more items by checking the checkbox or checkboxes concerned. For example, in the Font dialog box of any Microsoft Text editor like Microsoft Words, there are many checkboxes under the Effects section. The user can choose to underline, subscript, small caps, superscript, blink and etc.
In Visual Basic 2015, you can create a shopping cart where the user can click on checkboxes that correspond to the items they intend to buy, and the total payment can be computed at the same time.
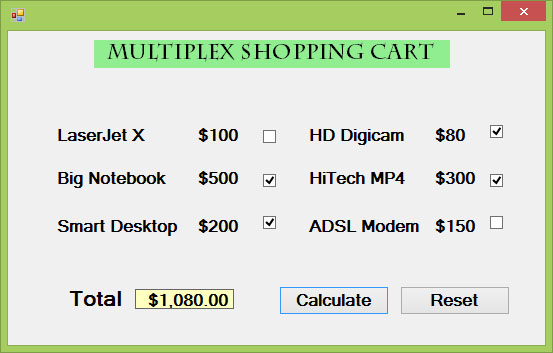
Example 21.1: Shopping Cart
In this example, we add a few labels, two buttons, and six checkboxes. We declare the price of each item using the Const keyword. If a checkbox is being ticked, its state is True else its state is False. To calculate the total amount of purchase, we use the mathematical operator +=. For example, sum+=BN is actually sum=sum+BN. Finally, we use the ToString is a Visual Basic 2015 method to display the amount in currency.
The Code
Public Class Form1
Private Sub BtnCal_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnCal.Click
Const LX As Integer = 100
Const BN As Integer = 500
Const SD As Integer = 200
Const HD As Integer = 80
Const HM As Integer = 300
Const AM As Integer = 150
Dim sum As Integer
If CheckBox1.Checked = True Then
sum += LX
End If
If CheckBox2.Checked = True Then
sum += BN
End If
If CheckBox3.Checked = True Then
sum += SD
End If
If CheckBox4.Checked = True Then
sum += HD
End If
If CheckBox5.Checked = True Then
sum += HM
End If
If CheckBox6.Checked = True Then
sum += AM
End If
LblTotal.Text = sum.ToString("c")
End Sub
Private Sub BtnReset_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnReset.Click
CheckBox1.Checked = False
CheckBox2.Checked = False
CheckBox3.Checked = False
CheckBox4.Checked = False
CheckBox5.Checked = False
CheckBox6.Checked = False
End Sub
End Class
Figure 21.1: Shopping Cart
Example 21.2
Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click Const large As Integer = 10.0 Const medium As Integer = 8 Const small As Integer = 5 Dim sum As Integer If CheckBox1.Checked = True Then sum += large End If If CheckBox2.Checked = True Then sum += medium End If If CheckBox3.Checked = True Then sum += small End If Label5.Text = sum.ToString(“c”) End Sub
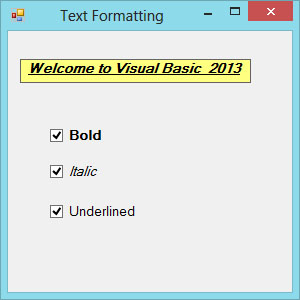
Example 21.3
In this example, the text on the label can be formatting using the three check boxes that represent bold, italic and underline.
The Code
Public Class Form1 Private Sub ChkBold_CheckedChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles ChkBold.CheckedChanged If ChkBold.Checked Then LblDisplay.Font = New Font(LblDisplay.Font, LblDisplay.Font.Style Or FontStyle.Bold) Else LblDisplay.Font = New Font(LblDisplay.Font, LblDisplay.Font.Style And Not FontStyle.Bold) End If End Sub Private Sub ChkItalic_CheckedChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles ChkItalic.CheckedChanged If ChkItalic.Checked Then LblDisplay.Font = New Font(LblDisplay.Font, LblDisplay.Font.Style Or FontStyle.Italic) Else LblDisplay.Font = New Font(LblDisplay.Font, LblDisplay.Font.Style And Not FontStyle.Italic) End If End Sub Private Sub ChkUnder_CheckedChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles ChkUnder.CheckedChanged If ChkUnder.Checked Then LblDisplay.Font = New Font(LblDisplay.Font, LblDisplay.Font.Style Or FontStyle.Underline) Else LblDisplay.Font = New Font(LblDisplay.Font, LblDisplay.Font.Style And Not FontStyle.Underline) End If End Sub End Class
* The above visual basic 2015 program uses the CheckedChanged event to respond to the user selection by checking a particular checkbox, it is similar to the click event. The statement
LblDisplay.Font = New Font(LblDisplay.Font, LblDisplay.Font.Style Or FontStyle.Italic)
will retain the original font type but change it to italic font style.
LblDisplay.Font = New Font(LblDisplay.Font, LblDisplay.Font.Style And Not FontStyle.Italic)
will also retain the original font type but change it to regular font style. (The other statements employ the same logic)
The Output
Figure 21.2