[Lesson 12] << [CONTENTS] >> [Lesson 14]
There are many built-in functions In Visual Basic 2012. In this lesson, you will learn a couple of built-in functions that deal with string manipulation.
13.1 The Mid Function
The Mid function is used to retrieve a part of the text from a given phrase. The syntax of the Mid Function is
Mid(phrase, position,n)
*phrase is the string from which a part of the text is to be retrieved
*position is the starting position of the phrase from which the retrieving process begins.
*n is the number of characters to retrieve.
Example 13.1
Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
Dim myPhrase As String
myPhrase = Microsoft.VisualBasic.InputBox("Enter your phrase")
Label1.Text = Mid(myPhrase, 2, 6)
End Sub
* This program will extract text starting from position 2 of the phrase and the number of characters extracted is 6.
The figures are shown below:

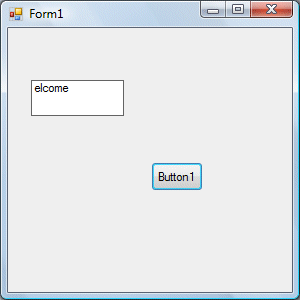
13.2 The Right Function
The Right function extracts the right portion of a phrase. The format is
Microsoft.Visualbasic.Right ("Phrase", n)
Where n is the starting position from the right of the phase where the portion of the phrase is going to be extracted. For example:
Microsoft.Visualbasic.Right ("Visual Basic", 4) = asic
Example 13.2
The following code extracts the right portion any phrase entered by the user.
Private Sub Button1_Click (ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click Dim myword As String myword = TextBox1.Text Label1.Text = Microsoft.VisualBasic.Right (myword, 4) End Sub
13.3 The Left Function
The Left function extracts the left portion of a phrase. The format is
Microsoft.Visualbasic.Right ("Phrase", n)
Where n is the starting position from the left of the phase where the portion of the phrase is going to be extracted. For example:
Microsoft.Visualbasic.Left("Visual Basic", 4) = asic
Example 13
The following code extracts the left portion any phrase entered by the user.
Private Sub Button1_Click (ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click Dim myword As String myword = TextBox1.Text Label1.Text = Microsoft.VisualBasic.Left (myword, 4) End Sub
13.4 The Trim Function
The Trim function trims the empty spaces on both sides of the phrase. The format is
Trim("Phrase")
.For example, Trim (” Visual Basic “) = Visual basic
Example 13.4
Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
Dim myPhrase As String
myPhrase = Microsoft.VisualBasic.InputBox("Enter your phrase")
Label1.Text = Trim(myPhrase)
End Sub
13.5 The Ltrim Function
The Ltrim function trims the empty spaces of the left portion of the phrase. The format is
Ltrim("Phrase")
.For example,
Ltrim (" Visual Basic 2012")= Visual basic 2012
13.6 The Rtrim Function
The Rtrim function trims the empty spaces of the right portion of the phrase. The format is
Rtrim("Phrase")
.For example,
Rtrim ("Visual Basic 2012 ") = Visual Basic 2012
13.7 The InStr function
The InStr function looks for a phrase that is embedded within the original phrase and returns the starting position of the embedded phrase. The format is
Instr (n, original phase, embedded phrase)
Where n is the position where the Instr function will begin to look for the embedded phrase. For example
Instr(1, "Visual Basic 2012 ","Basic")=8
*The function returns a numeric value.
You can write a program code as shown below:
Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click Label1.Text = InStr(1, "Visual Basic", "Basic") End Sub
13.8 The Ucase and the Lcase Functions
The Ucase function converts all the characters of a string to capital letters. On the other hand, the Lcase function converts all the characters of a string to small letters.
The syntax is
Microsoft.VisualBasic.UCase(Phrase) Microsoft.VisualBasic.LCase(Phrase)
For example,
Microsoft.VisualBasic.Ucase("Visual Basic") =VISUAL BASIC
Microsoft.VisualBasic.Lcase("Visual Basic") =visual basic
13.9 The Chr and the Asc functions
The Chr function returns the string that corresponds to an ASCII code while the Asc function converts an ASCII character or symbol to the corresponding ASCII code. ASCII stands for “American Standard Code for Information Interchange”. Altogether there are 255 ASCII codes and as many ASCII characters. Some of the characters may not be displayed as they may represent some actions such as the pressing of a key or produce a beep sound. The format of the Chr function is
Chr(charcode)
and the format of the Asc function is
Asc(Character)
The following are some examples:
Chr(65)=A, Chr(122)=z, Chr(37)=% ,
Asc("B")=66, Asc("&")=38